Androgenetic Hair loss
Androgenetic Hair loss
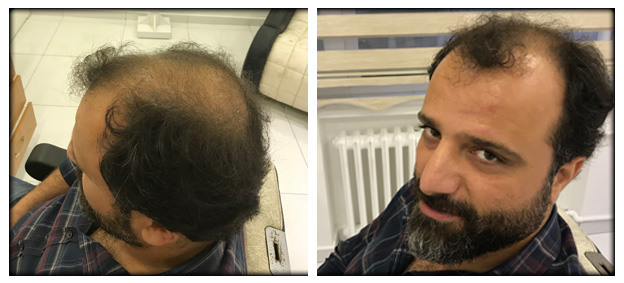
The most common type of hair loss is a condition called as androgenetic alopecia. Such hair loss can affect both men and women. For many people, hair loss is an annoying experience. Fortunately, there are treatments that help to regain hair or prevent hair loss. Hair follicle has a structure that surrounds the lower part of the hair shaft. Each follicle contains blood vessels that feed new hair growth.
● The growth phase of a single new hair stand lasts two to three years.
● At the end of such period, the growth stops and the follicle enters the resting phase.
● Three to four months after resting phase, hair begins to be lost and the next growth cycle begins.
About 80 to 90 follicles are growing on a normal scalp at any given moment. As the same number enters a new growth phase, about 75 follicles are lost every day. In men with androgenic alopecia, hormones associated with testosterone (also called as androgens) cause hair follicles to have a shorter growth phase, and they also cause abnormally short and thin hair shafts. It is stated that such follicles are "miniature". In general, although it is considered that the genetic background strongly influences the development of androgenetic alopecia in men, it is uncertain that how the family history affects any man's chance to develop hair loss.
Genetics play a role in the risk of androgenetic alopecia in women; however, any other factors (some of which are not known) can be important with respect thereto. For example, abnormal androgen levels in the blood are the reason for androgenetic alopecia in women on minimum basis. Additional researches are needed in order to better understand the genetic and any other roles of the androgenetic alopecia.
Despite being camouflaged in women, men and women experience androgenetic alopecia on an equal basis. In men, androgenetic alopecia is characterized by gradual hair thinning, which most commonly affects the crown and frontal areas of the scalp. Hair loss is a little more common than that of men; however, women can have similar hair loss patterns, and they rarely lose their entire hair.
Reasons Thereof in Women
Androgenetic Alopecia is the most common pattern of hair loss in women. Such kind of hereditary hair loss can start at any time after adolescence period, and it usually occurs before the age of 40. Women with androgenetic alopecia (AGA) usually cause an increase in hair loss or widespread hair loss.
Androgenetic Alopecia causes follicles to become sensitive to hormones or androgens that are already present in your body. Such follicles have androgen receptors. Androgens (hormones) instruct the androgen receptors to produce less hair. Consequently, the hair becomes thinner and delicate, and the cycles growing are shortened. Although there is no real loss of follicles, hair growth can eventually be stopped completely. In the follicle, there is an enzyme known as a 5 alpha-reductase. When the hormone (typically testosterone) binds to the androgen receptor, it triggers 5-alpha reductase in order to convert such testosterone into something called as DHT. DHT plays the most active role in damaging the hair generation. Therefore, "inhibition of DHT" means such a great sentence in the hair loss environments. Such androgens, and "anti-androgens", which inhibit DHT, and which manipulate DHT against such androgen process, are considered as legal hair loss treatments.
Reasons for Androgenetic Alopecia in Women
The reason for androgenetic alopecia in women is the genetic susceptibility. However, women have any other reasons for hair thinning. Incorporation of both growth stimulating and anti-androgens into a pretreatment regime is a very smart and effective method in order to overcome such problem today. There may be a large number of reasons for hair loss in women. Many conditions such as menstrual irregularities, hirsutism, acne, and testosterone levels increasing inherently may be factors associated with hair loss. Birth control pills are common, and pregnancy is the most common, and pre- and post-menopausal menopauses are completely hormonal-associated factors that can trigger hair loss from small to large. Stress can accelerate progression; however, if you have experienced stress, resulting in damage to your physical condition, for several months, then this is usually not the most obvious reason.
How is it diagnosed?
Androgenetic alopecia is usually diagnosed by examining the scalp. In some cases, you will need blood tests in order to investigate any other reasons for hair loss, such as changes in hormone levels, lower iron levels (anemia), or thyroid problems.
The psychosocial effects of hair loss may be severe for some people, especially for women, due to the fact that the situation cannot be quite understood, or that it is not accepted. Both women and men may have difficulties in low self-esteem.
How is it treated?
In respect of male pattern mud therapy in male, there are two drugs, which are minoxidil and finasteride. A drug called as minoxidil or spironolactone may be administered to women. Sometimes, finasteride is used in women who do not respond to any other treatments; however, it is not clear whether it is effective or not. In some cases, surgical options may also be considered. Androgenetic alopecia is a disease, which is diagnosed genetically, and which is characterized by gradual transformation of terminal hairs into a non-apparent state, and finally into vellus hair. It is a very common disease affecting both men and women.
Hemen Bilgi Al!
Formu doldurarak bilgi talebinde bulunabilirsiniz.
